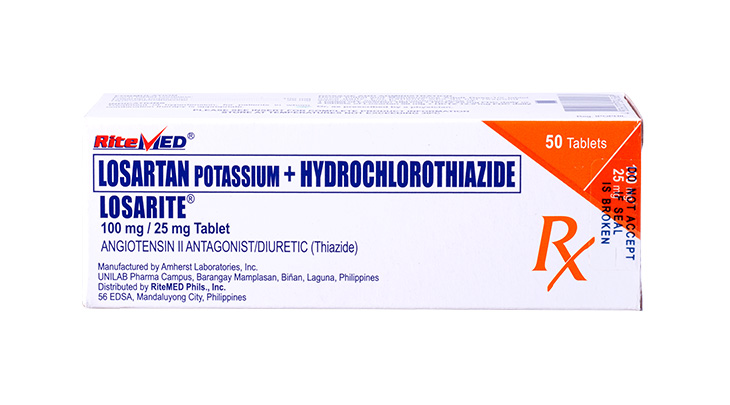
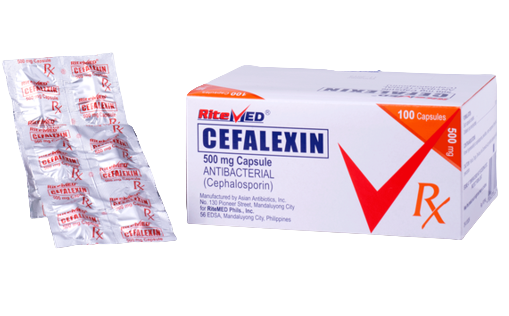
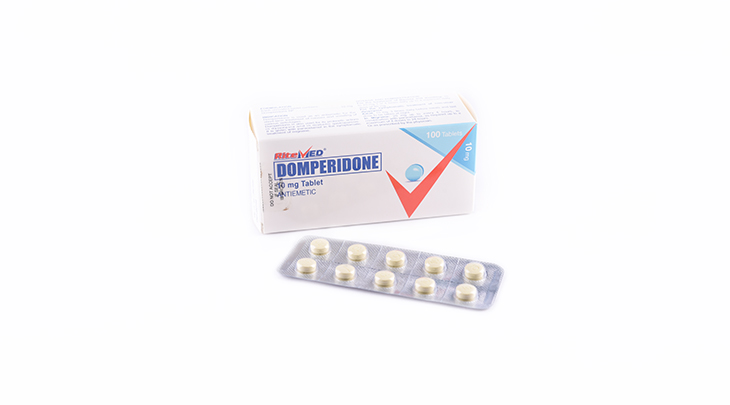
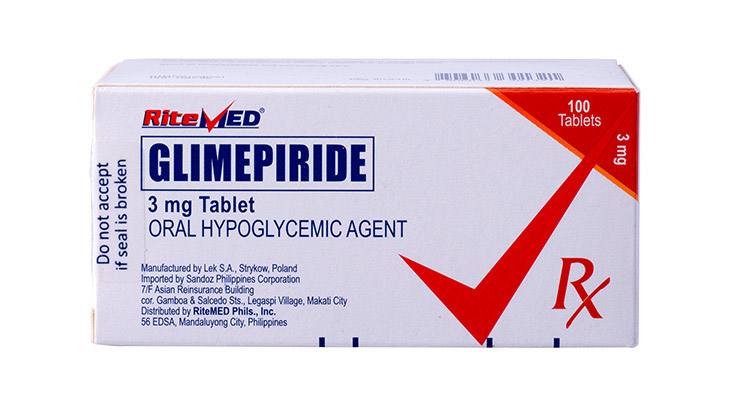
Product Details
What is this medicine used for?
For the relief of symptoms associated with seasonal, perennial, vasomotor rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis due to foods, parkinsonism (including drug-induced), short-term management of insomnia For the prevention and treatment of nausea, vomiting, and/or dizziness associated with motion sickness.
How much and how often should you use this medicine?
As an Antihistamine, Antitussive and Antiemetic
Orally, every 4 to 6 hours
Adults and Children 12 years and older: 10 to 20 mL (2 to 4 teaspoonsful)
Maximum Dose: 300 mg per day
Children 6 to 11 years: 5 to 10 mL (1 to 2 teaspoonsful)
Maximum Dose: 150 mg per day
2 to 5 years: 2.5 mL (1/2 teaspoonful)
Maximum Dose: 37.5 mg per day
For Antiparkinsonism
Orally, every 8 hours
Adults: 10 mL (2 teaspoonsful)
As Nighttime Sleep-Aid
Orally, 20 minutes before going to bed or after retiring when sleep is not readily achieved.
Adults and Children 16 years and older: 20 mL (4 teaspoonsful)
Do not take a second dose in the same night.
Do not exceed the stated dose.
If you continue to have sleeping problems for more than two weeks, talk to your doctor.
For the Prevention of Motion Sickness
Orally, every 4 to 6 hours
Adults and Children 12 years and older: 10 to 20 mL (2 to 4 teaspoonsful)
Maximum Dose: 300 mg per day
A dose should be given 30 minutes before exposure to motion; subsequent doses may be given before meals
and at bedtime for the duration of the exposure.
Children: 6 to 11 years: 5 to10 mL (1 to 2 teaspoonsful)
Maximum Dose: 150 mg per day
A dose should be given 30 to 60 minutes before travel.
Or, as recommended by a doctor.
Warnings and Precautions:
Do not use with any other product containing diphenhydramine, even one used on skin.
Driving and using machines: These medicines cause drowsiness. You should not drive or operate
machinery for at least 8 hours after taking these medicines.
As in adults, antihistamines may diminish mental alertness in children. In the young child, particularly, they may produce excitation. In elderly patients, antihistamines are more likely to cause dizziness, sleepiness, syncope (fainting), toxic
confusional states, sedation, and hypotension.
Undesirable Effects:
Diphenhydramine may cause drowsiness, dizziness, headache, disturbed coordination, depression, sleep
disturbances, tremor, convulsions, disordered sensations such as pins and needles, blood disturbances, liver
disturbances, hair loss, sweating, muscle pains, respiratory depression, digestive system disturbances, blurred vision, low blood pressure, palpitations, changed heart rhythms, urinary retention, bruising, dry mouth, nausea, and dry respiratory secretions. Uncommon side effects reported with diphenhydramine include acute dystonic reactions such as oculogyric crisis (rotation of the eyeballs), torticollis (contraction of neck muscles), and catatonia-like states, as well as allergic and photoallergic reactions.
Interaction w/ other medicaments:
Alcohol: Do not drink alcohol (wine, beer, spirits) while taking these medicines.
• Central Nervous System (CNS) depressants (barbiturates, tranquilizers, hypnotics, sedatives)
• Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) (phenelzine, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, furazolidone,
procarbazine)
• Atropine and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) (amitriptyline, doxepin, imipramine)